Healthgevity
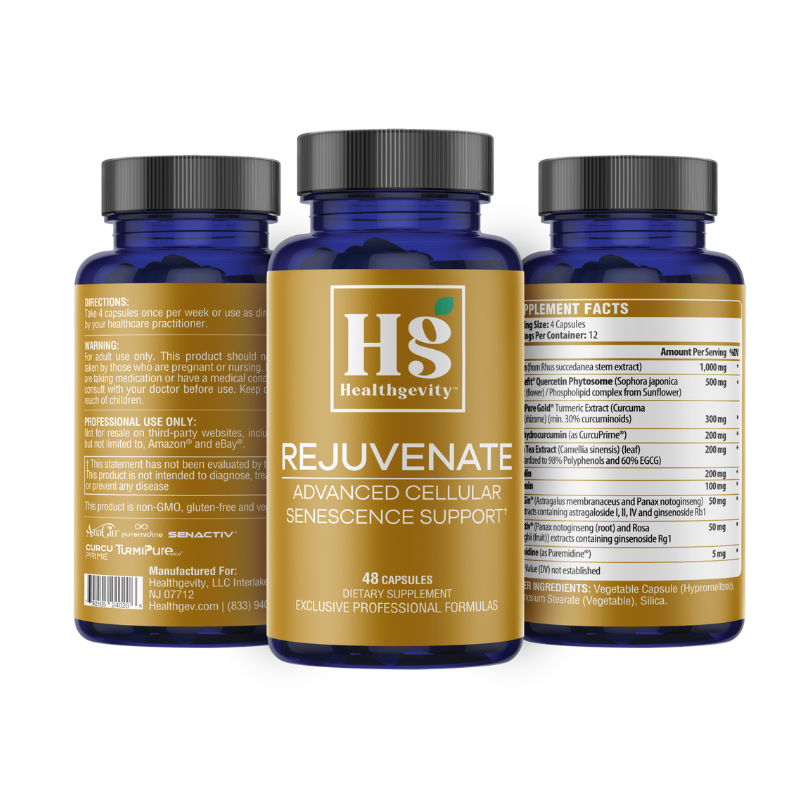
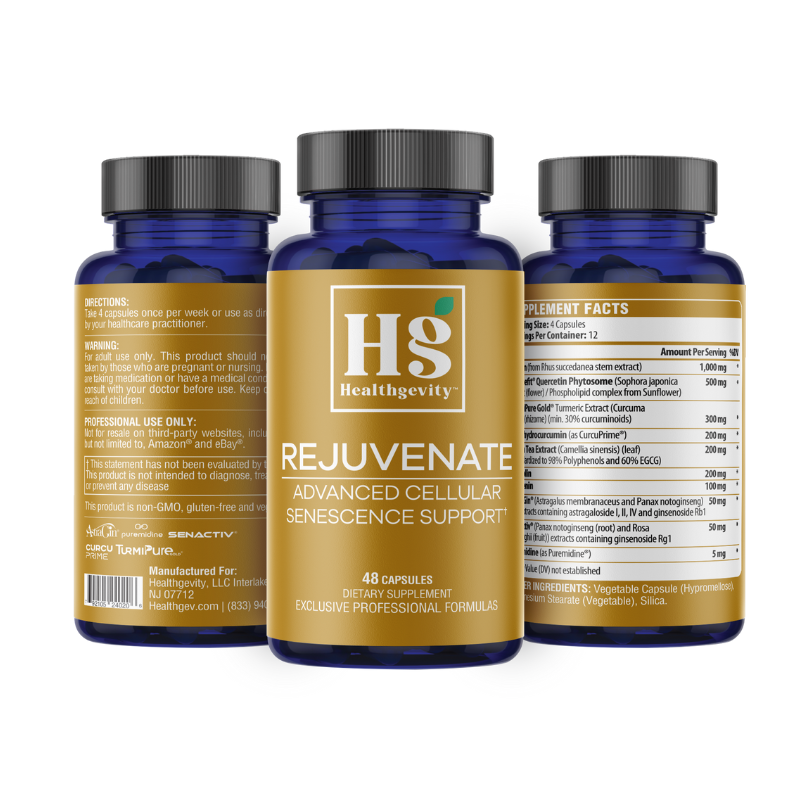
Rejuvenate (Senolytic)
Rejuvenate (Senolytic)
Couldn't load pickup availability
Cellular senescence is a hallmark of aging, it is a permanent state of cell cycle arrest induced by cellular stresses. This has numerous implications for the body, including its ability to adapt to changes in its environment, as well as its capacity to regenerate itself. This can be beneficial for individuals to understand how cellular senescence works and what the potential benefits are for the body. Firstly, understanding cellular senescence can help us better understand aging, as this process is a major contributor to the aging process. Additionally, it can also provide insight into certain diseases and conditions that may be linked to the inability of cells to divide and proliferate properly. Finally, by targeting cellular senescence, we may be able to find new ways of fighting against aging and diseases associated with it. Thus, understanding ways to best support cellular senescence can be a powerful tool in our pursuit of longevity and improved health span. Senolytics, are small molecules that can selectively kill senescence cells and have been developed to support various age-related diseases while also extending healthspan. In recent years, emerging natural compounds have been discovered to be effective senolytic agents that are featured in this breakthrough formula. Clearance of senescent cells can support the reduction of inflammation, decrease macromolecular dysregulation, and enhance function of stem and progenitor cells.
Rejuvenate presents a unique solution for intervention through two mechanisms:
(1) eliminating senescent cells (senolytics)
(2) inhibiting of senescent- associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
Featured benefits:
- Once weekly pulsed high dosing blend of senolytics which have been shown to reduce senescent cells in vivo.
- Targets aging at the cellular level
- Induces autophagy to promote intracellular recycling and cellular renewal
- Reduce full body features of Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP).
- Protects cells against free radicals and oxidative stress
- Targets inflammaging at the cellular level and supports a healthy inflammatory response
- Supports a healthy immune system
- Formula designed to also treat muscle senescence.
- Exercises muscles longer and harder with a boost in citrate synthase activity.
- Recovers more effectively with a reduction in inflammation biomarkers.
- Decreases SA-β-Gal by 63% in muscle tissue.
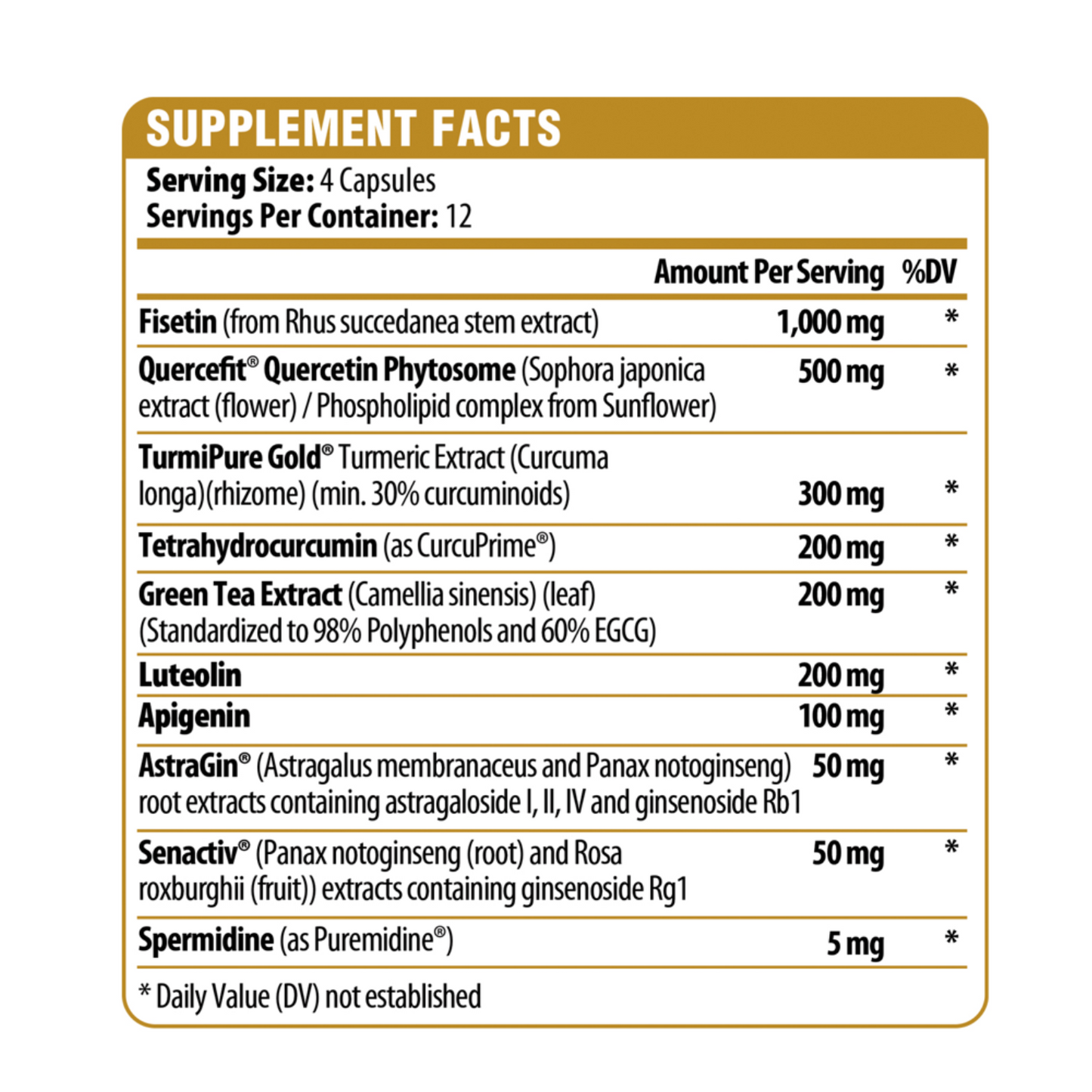
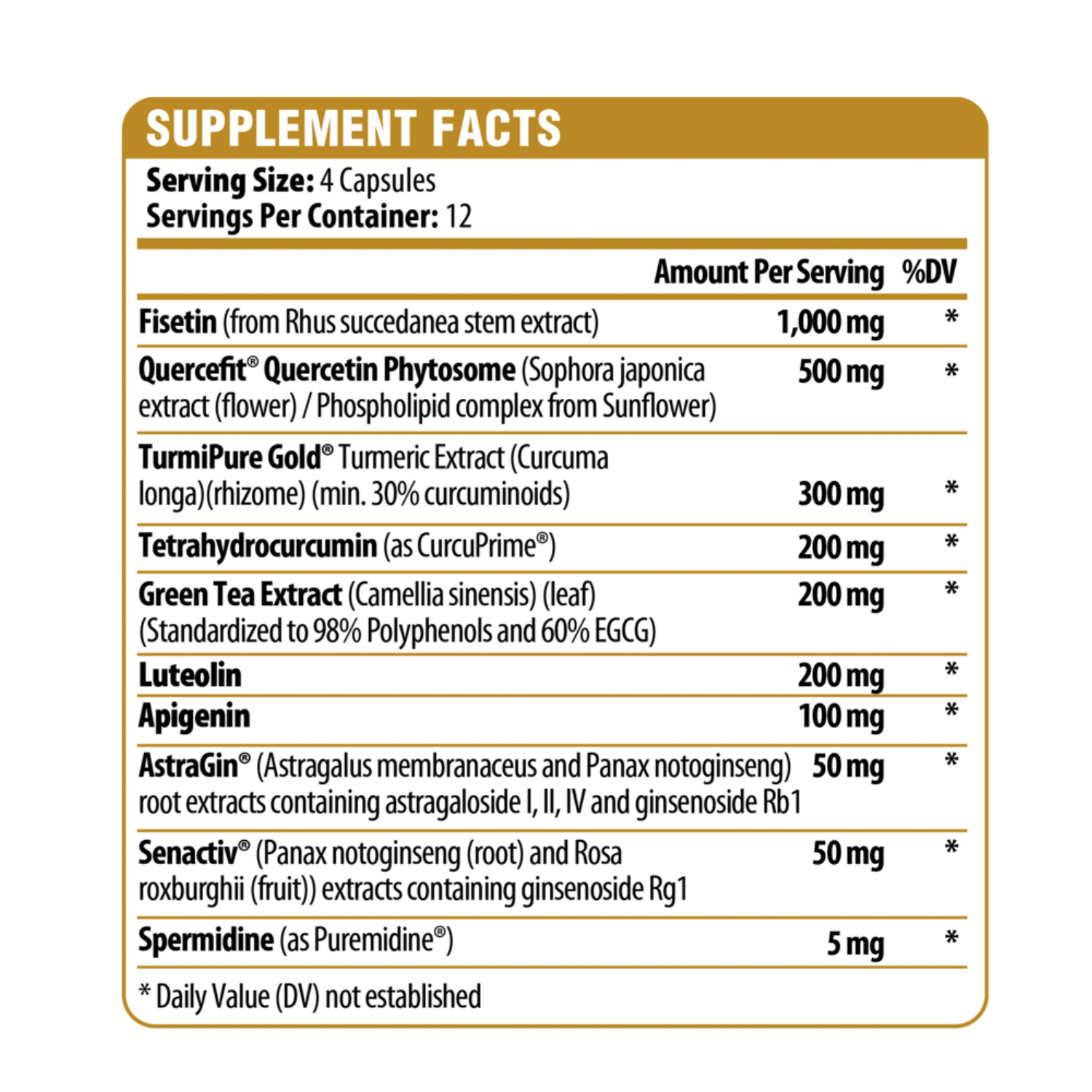
Fisetin:
Fisetin is a polyphenol found in many fruits and vegetables, including strawberries, apples, and onions. It has been studied for its potential benefits related to aging. Fisetin has shown great promise to inhibit senescence due to its ability to act on numerous biological processes. Studies have shown that fisetin is the most natural senolytic agent that can protect cells from oxidative damage, protecting them against age related diseases and reduce senescence markers in multiple tissues.
Quercetin Phytosome:
Quercetin is one of the most studied dietary flavonoids ubiquitously present in various vegetables. A key feature of quercetin is its strong antioxidant activity which potentially enables it to quench free radicals from forming resonance-stabilized phenoxyl radicals. However, chemical instability, poor water solubility and low bioavailability of quercetin greatly limit its applications which is why a phytosome technology is the preferred delivery system to overcome these limitations. This enhanced form of quercetin has been shown to be 20 times better absorbed than other quercetin options.
Spermidine:
Spermidine has emerged as an important metabolite that links cellular aging and autophagy. Spermidine is a naturally occurring polyamine involved in biological processes such as cell growth and proliferation, tissue regeneration and translation regulation, making it a critical regulator of cellular homeostasis. Spermidine also exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-aging properties. External supplementation of spermidine improves longevity, which may be attributed to its ability to exert cardioprotective and neuroprotective effects, as well as reducing immune senescence.
Senactiv® (Panax notoginseng (root) and Rosa roxburghii (fruit)) extracts containing ginsenoside Rg1:
Senactiv® promotes more energy and muscle preservation by activating phagocytic macrophages in association with the senescent cell clearance in muscle tissue after aerobic exercise. It's composed of two highly purified and fractionated extracts from Panax notoginseng and Rosa rugosa. Research suggests that this combination is a potent senolytic. Muscle samples taken before and after exercise shows that Senactiv® supplementation resulted in significantly fewer amounts of detectable β-galactosidase-tagged cells which is a method to assess cellular senescence. In a recent Senactiv® human clinical study confirmed, though exercise generally increases the movement of white blood cells and “clean up” cells into the muscle, it does not always activate phagocytosis to clear away the broken down apoptotic cells and senescent cells . With Senactiv®, phagocytosis activation can clear these types of cells away leading to the decrease in both apoptotic and senescent cells in active muscles.
TurmiPure GOLD®
Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) has been used in India for more than 5,000 years as a spice and medicinal herb in traditional ayurvedic medicine. Well-known for its anti-inflammatory properties, it is now recognized as the #1 botanical for healthy aging. However, its poor bioavailability (number of actives reaching the blood stream) in curcuminoids lowers its efficacy and its poor solubility limits its application (often limited to capsules and tablets), therefore high intake (~1500mg) of standard turmeric extract was shown to be efficient.
After 5 years of research, our partner has overcome these issues by developing TurmiPure GOLD®, the world’s first bioequivalent turmeric at a low dose of 300mg. Its innovative formulation highly enhances the bioavailability of curcuminoids 24X, in addition to being instantly water dispersible. A dose of 300mg of TurmiPure Gold® delivers as many curcuminoids in blood as 1922mg of standard turmeric 95% curcuminoids (with or without addition of 1% black pepper extract standardized to 95% piperine). Curcuminoids are clinically proven to be effective in more than 100 studies to support: healthy joint function (including inflammatory response), normal bile production and overall body function, contributing to healthy aging conditions. Curcumin has shown promise to mitigate the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) and its aging-induction consequences of senescent cells.
Tetrahydrocurcumin (CurcuPrime®)
Tetrahydrocurcumin (4-HC) is the key bioactive derivative of curcumin and with advances in science, it’s also given credibility as the engine behind all that curcumin brings to the table. With a newfound ability to extract and isolate the compound, research has even seen tetrahydrocurcumin outperform its parent compound in several tests of its capabilities. Researchers have also confirmed that 4-HC attenuated pro-inflammatory indicators like interleukin-1, interleukin-6, TNF-⍺, and prostaglandin E2.
Apigenin:
Apigenin is a natural bioactive plant polyphenol with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immune system boosting properties. It also helps to support against oxidative stress for better cellular function. Studies have shown that apigenin prevents excessive loss of NAD+ by reducing the amount of circulating CD38, allowing NAD+ stores to remain at higher, more youthful levels. Apigenin is known to induce apoptosis in a p53-independent pathway by enhancing oxidative stress. The p53-independent apoptotic effects of apigenin would support its use as a senolytic
Luteolin:
Luteolin is a flavonoid naturally found in plants. Flavonoids like luteolin have been found to have beneficial effects on human health by reducing oxidative stress. Luteolin, which acts as the first-line defense system in plants against adverse photobiological effects such as protection against UV radiation, has shown promising senotherapeutic effects
Green Tea containing epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
The phytochemical epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the major catechin found in green tea, with many potential benefits on health outcomes, including cell senescence, aging, and age-related diseases. Preclinical evidence suggests that EGCG exhibits promising senolytic and senomorphic effects through multi-faceted mechanisms, including targeting apoptotic pathways, cell cycle regulation, nutrient sensing pathways, SASP, and oxi-inflammatory stress pathways.
AstraGin® (Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng) root extracts containing astragaloside I, II, IV and ginsenoside Rb1:
AstraGin® is a proprietary plant derived compound complex extracted by a proprietary pharmaceutical extraction and processing technology. AstraGin® upregulates mRNA and protein expression levels of nutrient transporters that regulate the absorption of nutrients and plant compounds in the gut. AstraGin® has shown in 16 in-vitro and 8 in-vivo studies that are published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, Molecular Nutrition & Food Research and Scientific Reports to:
- Increase the absorption of peptides, amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins, and phytonutrients by up regulating the absorption specific mRNA and transporters, such as SGLT1, CAT1, and GLUT4. One example is AstraGin® has been shown to increase curcumin absorption by 92%.
- Repair ulcerated and damaged intestinal walls and reduce intestinal submucosa inflammation. AstraGin® was shown in a hematoxylin-eosin stain and a MPO assay to reduce ulceration and unclear surfaces of intestinal epithelial cells and sub-mucosal edema in TNBS- induced colitis rats.
- May help maintain a healthy microbiota population by mending ulcerated and damaged intestinal epithelial cell surfaces for the microbiota to populate.
- May help support stronger immune functions by mending ulcerated epithelial cells and reducing the inflammation in intestinal mucosal lamina propria that hosts the gut- associated lymphoid tissue (GALT1), T cells, plasma cells, mast cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages.
Share